Driving Sustainable Rail Infrastructure Through EU Taxonomy Alignment
Start Reading

1. Company at a Glance
In this case study, we explore how Adif Alta Velocidad used the EU Taxonomy not just as a compliance requirement, but as a strategic lever to strengthen its sustainability leadership in the rail sector.Adif Alta Velocidad is Spain’s state-owned railway infrastructure manager, responsible for the development, maintenance, and operation of the country’s highspeed rail network.
Recognizing the role of rail infra-structure in climate mitigation, the company undertook a comprehensive internal process to assess, validate, and report the alignment of its activities with the Taxonomy framework. Through robust data governance, cross depart-mental collaboration, and alignment with its 2030 Strategic Plan, Adif Alta Velocidad was able to demonstrate the high sustainability value of its projects— facilitating access to green finance and enhancing its credibility among investors.
2. The Challenge
Adif Alta Velocidad (Adif AV) launched its EU Taxonomy alignment initiative in response to both a regulatory requirement and a strategic opportunity. As the manager of Spain’s General Interest Railway Network, the company recognized its critical role in decarbonizing the transport sector. The initiative stems from the need to comply with the EU Regulation 2020/852 and related delegated acts, which require companies to assess and disclose the sustainability of their activities.
Beyond compliance, Adif AV viewed the Taxonomy as a tool to transparently demonstrate rail’s systemic value in the transition to a low-carbon economy. By aligning its infrastructure investments—particularly in electrification, modernization, and climate resilience— with Taxonomy criteria, the company aims to unlock sustainable finance, reduce its carbon footprint, and facilitate modal shift from more polluting modes of transport. The initiative also supports the company’s broader strategic goals under its 2030 Strategic Plan, reinforcing its commitment to the European Green Deal and the Paris Agreement.

3. The Action
To align with the EU Taxonomy and strengthen its role in the green transition, Adif Alta Velocidad developed a robust and multi-phase action plan:
Strategic Alignment and Regulatory Compliance
In response to Regulation (EU) 2020/852 and its delegated acts, Adif Alta Velocidad launched an internal process to evaluate the environmental sustainability of its activities. The initiative was fully integrated into the company’s 2030 Strategic Plan, aligning with key challenges such as climate change, resilience, and sustainable mobility.
Governance Framework and Internal Coordination
A dedicated governance system was established to coordinate the flow of financial and non-financial data, identify responsibilities across departments, and ensure the validation of sustainability information. The initiative fostered unprecedented collaboration between operational, financial, and environmental teams.
Methodological Framework for EU Taxonomy Compliance
The company adopted a hybrid methodological approach—quantitative and qualitative— guided by the recommendations of the Platform on Sustainable Finance. The focus was on evaluating activities under category 6.14 (railway infrastructure management), enabling high eligibility and alignment results
Evaluation of Minimum Social Safeguards
The company reviewed its practices against the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) to ensure compliance with minimum social safeguards, as outlined under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
Capacity Building and Technical Support
Specialized training was provided to departments unfamiliar with sustainability frameworks, ensuring consistent interpretation and implementation. Technical experts also supported the development of annual Taxonomy reports in collaboration with the sustainability team.
Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
Adif actively communicated results to investors and stakeholders through newsletters and annual sustainability reports. The information was made publicly available on its corporate website to promote transparency and attract sustainable finance.
Integration with EU Funding Mechanisms
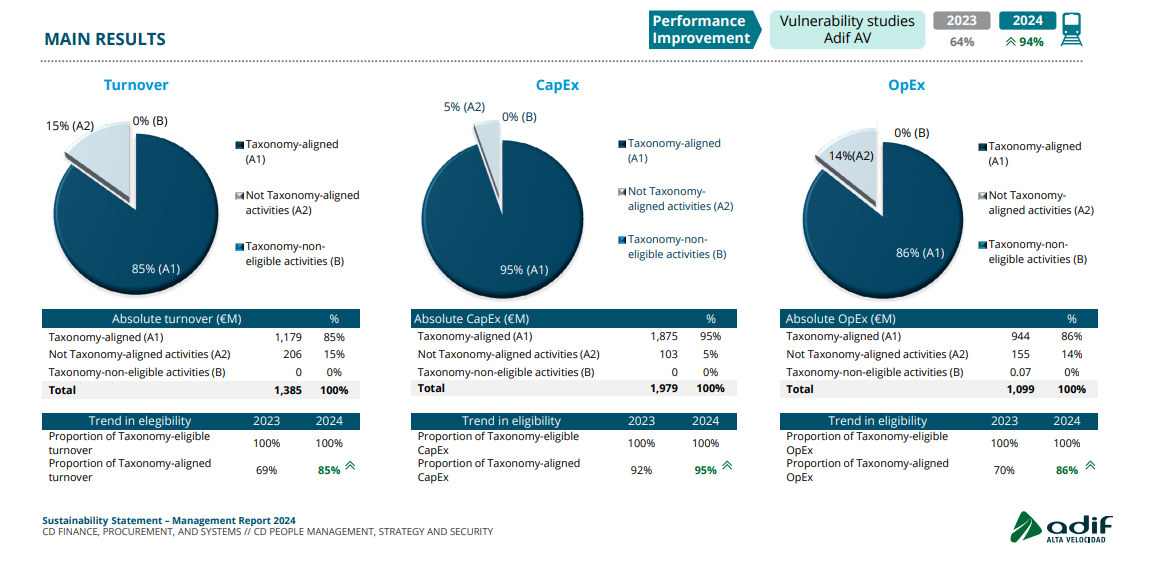
The initiative was closely linked to the Recovery and Resilience Mechanism (RRM), facilitating access to European funds such as Next Generation EU and ERDF. This accelerated the development of climate vulnerability studies, which expanded from 64% coverage in 2023 to 94% in 2024.
Planning for Continuous Improvement
Looking ahead, Adif plans to implement a Sustainability Information Internal Control System (SCIIS) to further enhance data traceability, consistency, and governance. Efforts will continue to improve DNSH documentation and expand stakeholder communication.

4. Overcoming Barriers
Connecting financial and environmental data
One of the main challenges was integrating financial information with environmental and sustainability parameters. This required new cross-departmental collaboration between teams that traditionally operated separately—financial, environmental, and railway operations. The creation of new workflows was key to meeting the complex data requirements of the Taxonomy framework.
Demonstrating compliance with DNSH criteria
Particularly difficult was the documentation of “Do No Significant Harm” (DNSH) criteria, especially for climate adaptation and waste management from construction activities. In some cases, the lack of structured data made it difficult to validate alignment. Adif AV responded by improving technical data quality and availability and strengthening analytical procedures in subsequent reporting cycles.
Managing construction waste in line with circular economy principles
The company developed internal procedures to ensure that surplus construction materials are reused in line with Spanish legislation (Law 7/2022) and that non-reusable waste is handled by authorized waste managers. In 2023, the corporate waste management model was updated to address the complex task of managing legacy railway waste.
Building internal capacity and shared understanding
Some departments were unfamiliar with the regulatory parameters introduced by the Taxonomy. To address this, targeted internal training was provided to build a shared language, improve understanding of EU sustainability frameworks, and ensure consistent application of sustainability criteria across the company

5. Impacts & Results
The integration of EU Taxonomy criteria has delivered tangible results for Adif Alta Velocidad, reinforcing its environmental leadership in the rail sector:
Full Eligibility Achieved
100% of CapEx, OpEx, and turnover classified as eligible under the EU Taxonomy
High Alignment Levels
In 2024, 85% of turnover aligned with Taxonomy requirements, demonstrating the strong contribution of highspeed rail to climate mitigation.
Increased Access to Sustainable Finance
The results supported the issuance of green bonds worth €500 million, expanding funding opportunities for future projects
Improved Transparency and Investor Confidence
Providing clear, verifiable environmental metrics strengthened Adif Alta Velocidad’s reputation in sustainability indices and with institutional investors. Sustainalytics awarded the company a score of 4.3 in May 2024, ranking first among 175 transport infrastructure peers and third globally out of more than 15,000 companies. MSCI also upgraded the company’s ESG rating to BBB in 2025, continuing a positive trend from previous years.
Enhanced Internal Governance and Collaboration
The initiative helped establish a Sustainability Policy and a dedicated Sustainability Committee in 2024, driving stronger coordination across departments. As a result, environmental considerations are increasingly embedded in day-to-day operations
6. Key Lessons Learned

"Integrating the EU Taxonomy was not just a compliance exercise—it became a catalyst for internal transformation. By aligning financial and environmental data, strengthening governance, and fostering cross-departmental collaboration, we laid the groundwork for long term sustainable growth. Start early, build shared understanding, and see regulation as a roadmap, not a barrier.”
Adif Alta Velocidad Sustainability Team
7. Recommended Resources
Recommended UN Global Compact resources available to support your journey:
Download Case Study
Disclaimer: This case example is intended strictly for learning purposes and does not constitute an endorsement of the individual companies by the UN Global Compact.


